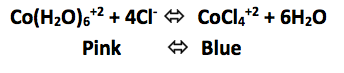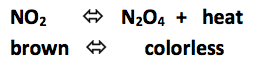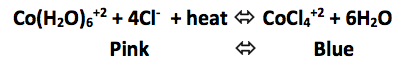Virtual Lab: Le Chatelier's Principle Inquiry
BACKGROUND: Equilibrium exists when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. When a stress is added to the reaction, the rates are no longer equal. The reaction will proceed in such a way to make the rates back to equal and establish a new equilibrium. This is known as LeChatelier’s principle.
PURPOSE: Observe stress on reactions and record the shift that the reaction undergoes to relieve the stress.
PRE LAB:
- Define Equilibrium.
- When a system is at equilibrium, are the concentrations equal or constant?
PROCEDURE:
For each experiment, click to see the effect of various stressors on equilibrium and record your observations. Then analyze your results and complete the conclusion questions.
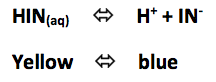
Click to add HCl (increase the H+ concentration) then add NaOH (decrease the H+ concentration)
Increasing the H+ concentration shifted the reaction to the ______________________
Decreasing the H+ concentration shifted the reaction to the _____________________
Increasing the H+ concentration shifted the reaction to the ______________________
Decreasing the H+ concentration shifted the reaction to the _____________________
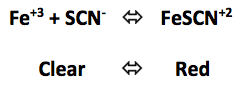
Click to add KSCN (increase SCN- concentration)
Click to add Fe(NO3)3 (increase Fe+3 concentration)
Click to add Na2HPO4 (decrease Fe+3 concentration)
Increasing the SCN- concentration shifted the reaction to the _______________________
Increasing the Fe+3 concentration shifted the reaction to the _______________________
Decreasing the Fe+3 concentration shifted the reaction to the ______________________
Click to add Fe(NO3)3 (increase Fe+3 concentration)
Click to add Na2HPO4 (decrease Fe+3 concentration)
Increasing the SCN- concentration shifted the reaction to the _______________________
Increasing the Fe+3 concentration shifted the reaction to the _______________________
Decreasing the Fe+3 concentration shifted the reaction to the ______________________
Click to add 12M HCl (increase Cl- concentration)
Click to add AgNO3 (decrease Cl- concentration)
Increasing the Cl- concentration shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the Cl- concentration shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Click to add AgNO3 (decrease Cl- concentration)
Increasing the Cl- concentration shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the Cl- concentration shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Click to place test tube in hot water bath. (increase heat)
Click to place test tube on ice. (decrease heat)
Increasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ___________________
Click to place test tube on ice. (decrease heat)
Increasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ___________________
Click to place test tube in a hot water bath. (increase heat)
Click to place test tube on ice. (decrease heat)
Increasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ___________________
Click to place test tube on ice. (decrease heat)
Increasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ____________________
Decreasing the heat shifted the reaction to the ___________________
CONCLUSION:
Upon analyzing your results:
Upon analyzing your results:
- When the concentration of a substance was increased, equilibrium shifted away or towards that side of the reaction?
- When the concentration of a substance was decreased, equilibrium shifted away or towards that side of the reaction?
- When the temperature was increased, equilibrium shifted away or towards the side of the reaction that contains the heat?
- When the temperature was decreased, equilibrium shifted away or towards the side of the reaction that contains the heat?